Unlocking Half-Bridge Drivers: A Comprehensive Guide
In modern power electronics systems, half-bridge drivers play a crucial role. They are widely used in various fields, including electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, industrial automation, and consumer electronics. Half-bridge drivers control two switching devices (usually MOSFETs or IGBTs) to effectively control inductive loads such as motors and electromagnets.
Detailed Explanation of H-Bridge Drivers
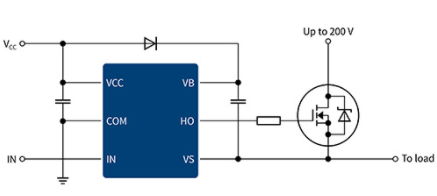 An H-Bridge Driver is a type of driver used for full-bridge circuits, while a half-bridge driver is its simplified form, specifically designed for half-bridge circuits. A half-bridge circuit consists of two switching devices and is commonly used in power conversion and motor driving applications. The primary function of a half-bridge driver is to receive pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals from a controller, amplify them, and convert them into signals suitable for driving MOSFETs or IGBTs.
An H-Bridge Driver is a type of driver used for full-bridge circuits, while a half-bridge driver is its simplified form, specifically designed for half-bridge circuits. A half-bridge circuit consists of two switching devices and is commonly used in power conversion and motor driving applications. The primary function of a half-bridge driver is to receive pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals from a controller, amplify them, and convert them into signals suitable for driving MOSFETs or IGBTs.
The working principle of a half-bridge driver is based on the control of high-side and low-side switches. The high-side switch is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, while the low-side switch is connected to the ground. By controlling the conduction and cutoff of these two switches, voltage control of the load can be achieved. To avoid the shoot-through phenomenon caused by simultaneous conduction of the high-side and low-side switches, half-bridge drivers typically provide dead-time control.
Common types of H-Bridge Drivers based on their functions, application scenarios, and technical features include:
● Non-Isolated Half-Bridge Drivers: These types of drivers are typically used in low-voltage systems, such as AC/DC converters, power tools, and low-voltage DC/DC converters. They achieve high-side and low-side driving through level shifting.
● Isolated Half-Bridge Drivers: Isolated drivers achieve signal isolation through optocouplers or pulse transformers and are suitable for high-voltage systems. These drivers can effectively prevent voltage interference between the high-side and low-side.
● Integrated Half-Bridge Drivers: Integrated half-bridge drivers combine the high-side and low-side driving circuits into a single chip, featuring small size and high reliability.
Half-bridge drivers, with their efficient and flexible characteristics, have found widespread applications in multiple fields. In electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), half-bridge drivers are used in motor controllers and DC/DC converters, significantly enhancing energy efficiency and system reliability, and aiding in power transmission and energy management of the vehicles. In the field of industrial automation, half-bridge drivers are extensively used in motor driving and power conversion equipment, achieving efficient and stable production processes through precise control. Additionally, in the consumer electronics sector, such as in brushless DC motor drives for home appliances, half-bridge drivers can effectively reduce the size and weight of the PCB while optimizing energy efficiency, meeting the dual demands of modern electronic products for miniaturization and high performance.
Popular Half-Bridge Driver Models
Model | Supplier | Features |
UCC27282-Q1 | Texas Instruments | 3A, 120V half-bridge driver with 5V under-voltage lockout (UVLO), interlock, and enable functions |
Texas Instruments | 2.6A, 110V half-bridge driver with enable and interlock functions | |
LTC7063 | Analog Devices | High-voltage half-bridge driver for high-voltage, high-current applications with adaptive shoot-through protection |
NSD1624 | NOVOSENSE | Half-bridge driver for AC/DC converters, motor drives, and automotive DC/DC converters |
Selection Considerations for H-Bridge Drivers
1. High-Side Voltage: The high-side switch will bear the entire power supply voltage, so the driver must be able to safely handle this voltage.
2. Common-Mode Transient Immunity (CMTI): During fast switching operations, high voltage differences and noise may occur between the high-side and low-side switches. Selecting a driver with high CMTI characteristics is crucial.
3. Peak Drive Current: For high-power designs, the driver needs to provide high peak current to quickly charge and discharge the MOSFET gate capacitance.
4. Dead Time: To avoid shoot-through phenomena, selecting a driver with configurable dead time is recommended.
Conclusion
Half-bridge drivers are indispensable in modern power electronics systems. They achieve efficient and reliable power conversion and motor driving by precisely controlling high-side and low-side switches. With the rapid development of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, the demand for half-bridge drivers will continue to grow. Selecting the appropriate half-bridge driver requires a comprehensive consideration of application scenarios, voltage range, power requirements, and protection functions.
Website: www.conevoelec.com
Email: info@conevoelec.com